How Cars Actually Work: Engines, Brakes, and Transmissions Explained Simply
In 2026, with hybrids, EVs, and flex-fuel options popping up, the basics still rule most roads – especially our popular petrol and diesel rides. As someone who’s tinkered with cars and loves explaining them over chai, let’s break it down simply, no engineering degree needed. We’ll use everyday Indian examples to make it relatable. Ready? Let’s rev up!
The Heart of Your Car: How Engines Actually Work
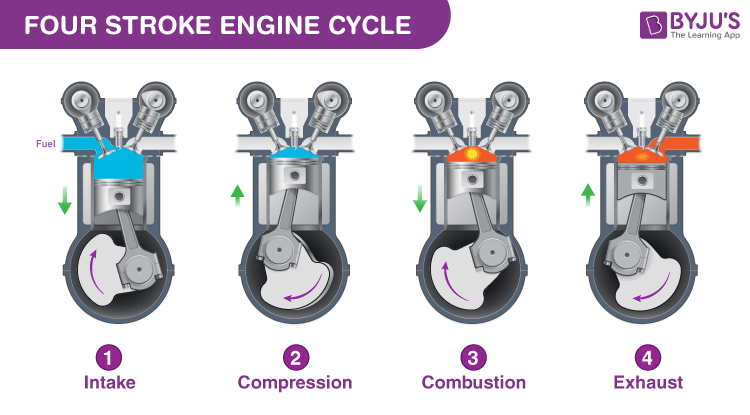
The engine is basically your car’s power plant – it turns fuel into motion. Most cars on Indian roads (like the Tata Punch, Nexon, or Maruti Swift) use a four-stroke internal combustion engine. Here’s the magic in four easy steps:
- Intake – Piston goes down, sucks in air + fuel mix.
- Compression – Piston rises, squeezes the mix tight.
- Power – Spark plug ignites it – boom! Explosion pushes piston down hard.
- Exhaust – Piston goes up again, pushes out waste gases.
This cycle repeats thousands of times per minute, turning up-and-down piston motion into spinning power via the crankshaft – which then spins your wheels!
Here are some clear diagrams showing the famous four-stroke cycle in action – super helpful to visualize:
In diesel cars (common in SUVs like Mahindra XUV700), no spark plug – high compression alone ignites the fuel. Petrol engines (like in Swift or Nexon petrol variants) love that spark for quick response.
Pro tip: That’s why regular servicing keeps your engine happy – clean air filter means better “breathing”!
Stopping Power: How Brakes Actually Work
You slam the brake pedal in monsoon traffic – and your car stops safely. But how?
Modern cars use hydraulic disc brakes (mostly front, sometimes all wheels). When you press the pedal, it pushes brake fluid through pipes to calipers at each wheel. The fluid squeezes brake pads against a spinning metal disc (rotor) attached to the wheel. Friction turns your car’s speed (kinetic energy) into heat – and boom, you slow down or stop.
Front brakes do most work because your car’s weight shifts forward when braking.
Check out this simple disc brake diagram – see how pads clamp the rotor like a powerful handshake:
Many Indian cars now have ABS (anti-lock braking) – it prevents wheels from locking so you can steer while braking hard. Life-saver on wet roads!
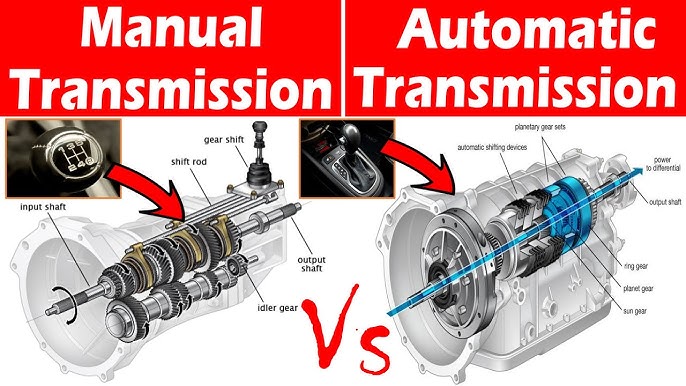
Gear Magic: How Transmissions Actually Work (Manual vs Automatic)
The transmission (gearbox) connects engine power to wheels and lets you change speed without over-revving or stalling.
Manual transmission (still loved in budget cars like older Swifts): You use clutch + gear stick to shift. Clutch disconnects engine from wheels momentarily so gears mesh smoothly. You control everything – great fun on highways!
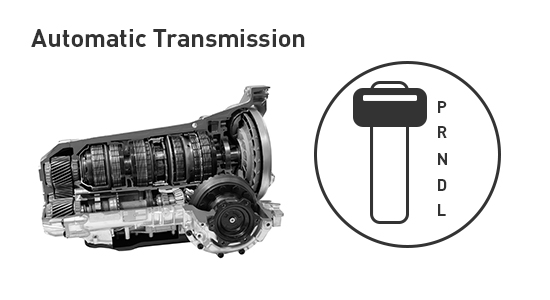
Automatic transmission (now super common in Nexon, Creta, etc.): No clutch pedal! A torque converter (fluid coupling) does the disconnecting, and computers/planetary gears shift automatically based on speed and throttle. Easy in city traffic!
Here are visuals comparing manual vs automatic gearboxes – spot the differences:
In 2026 India, automatics rule urban drives – less clutch wear in jams!
Why This Knowledge Matters for Indian Drivers
Understanding how cars actually work – engines turning fuel into power, brakes using friction to stop, transmissions matching speed to power – helps you drive smarter, spot issues early, and appreciate the engineering in your daily ride (whether it’s a zippy Swift or rugged Nexon).